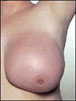
An uncommon type of invasive breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer represents only about 1% to 3% of all breast cancers. Inflammatory breast cancer involves the formation of either sheets or networks of cancer cells, rather than the development of a solid tumor. Inflammatory breast cancer is relatively aggressive in its growth.
Signs and symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include the following changes in the skin of the affected breast:
• A red, inflamed appearance
• A pitted (ie., dimpled) or ridged appearance
• A thick appearance
• Feeling warm to the touch
The changes in appearance and warmth are not the result of infection, but are caused by breast cancer cells blocking lymph vessels or channels in the breast tissue and skin of the breast.
Because inflammatory breast cancer does not involve the formation of any lumps, inflammatory breast cancer tends to be more difficult to recognize. In addition, women with inflammatory breast cancer can have normal mammograms and normal ultrasound examinations, which also can delay or confuse diagnosis.
Diagnosis is further complicated by the fact that inflammatory breast cancer and several other breast conditions have similar symptoms:
A bumpy, orange-peel-like texture of the skin
Redness
Swelling
The disorders in which symptoms similar to those of IBC occur include the following non-cancerous conditions:
Mastitis, a non-cancerous infection in the milk ducts. Mastitis is most common in younger women, especially those who are breast feeding.
A breast infection (breast abscess).
Mammary duct ectasia, a non-cancerous condition that typically occurs during or after menopause.
Dermatitis, an inflammation of the skin
|
 |
Laboratory diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer is performed via a biopsy, which involves taking a small amount of tissue and examining it under the microscope. |


