Once you have been diagnosed, the first things you and your doctor need to do are to determine what type of breast cancer you have, and learn how far the cancer has spread in your body (i.e.: what stage of cancer you have). Doctors have established a staging system, which will help both of you better understand your particular breast cancer. Remember, no two breast cancers are alike, so it is important to learn all of the attributes and unique characteristics of your breast cancer to help determine treatment options.
The stages of breast cancer include:
Stage 0: Carcinoma (breast cancer) in situ. Stage 0 breast cancer is non-invasive, meaning that it is contained within the ducts or lobules in the breast and has not spread to the surrounding tissue. There are two types of this early cancer, DCIS and LCIS. These early types of cancer account for about 15% to 20% of all breast cancer cases.
Stage I: The breast cancer is no larger than 2 centimeters and has not spread outside the breast.
Stage II: Breast cancer that is categorized as Stage II fits into one of the following three descriptions:
*The cancer is no larger than 2 centimeters, but has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm (i.e.: the axillary lymph nodes).
*The cancer is between 2 and 5 centimeters, and may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
*The cancer is larger than 5 centimeters, but has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
Stage IIIA cancers fit either one of two descriptions:
*The cancer is smaller than 5 centimeters and has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm, and the lymph nodes are attached to each other or to other structures.
*The cancer is larger than 5 centimeters and has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm.
Stage IIIB cancers fit one of either 2 descriptions, based on the degree of spread:
*The cancer has spread to the tissues near the breast (i.e.: the chest wall, including the ribs and the muscles in the chest)
*The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes inside the chest along the breast bone.
Inflammatory Breast Cancer: This very aggressive type of cancer also is categorized as a Stage IIIB. The unique quality of inflammatory breast cancer is that it makes the breast look red and inflamed. The redness may make the breast even warm to the touch.
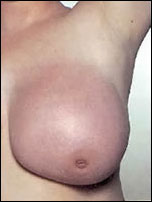
Because the skin of the breast often looks rough and dimply, like the peel of an orange, the appearance is termed peau d’orange. Inflammatory breast cancer may be misdiagnosed as a simple infection.
Stage IV: Stage IV breast cancers refer to either one of two descriptions, based on the degree of spread:
*The cancer has spread locally to the skin and lymph nodes inside the neck and near the collarbone.
*The cancer has spread to other organs of the body, most often the lungs, bones, liver, and brain.
Recurrent: In this stage, the cancer has returned after treatment. Breast cancer may recur in the breast, or in the soft tissue of the chest, or in another part of the body.
|


